A glenoid labrum tear involves damage to the shoulder’s cartilage, causing pain and instability. This injury can result from trauma, such as a fall or dislocation, or repetitive motion like overhead throwing. In this post, we’ll cover the symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Key Takeaways
- The glenoid labrum stabilizes the shoulder joint by deepening the socket and distributing forces evenly.
- Tears may occur due to acute trauma or repetitive motion, causing pain, instability, and limited motion.
- Treatment options range from conservative methods (physical therapy, activity modification) to surgical interventions.
Understanding the Glenoid Labrum
The glenoid labrum is a cup-shaped rim of fibrocartilage that deepens the glenoid cavity (shoulder socket) and stabilizes the joint. This structure maintains the integrity of the ball-and-socket joint, preventing dislocations and enabling pain-free movement.
Anatomy of the Glenoid Labrum
Encircling the glenoid cavity, the glenoid labrum anchors ligaments. While the specific shape varies, it’s typically 3 mm thick with a triangular upper shape and rounded lower profile. The labrum also attaches to the rotator cuff tendons and muscles, which are essential for shoulder movement and stability.
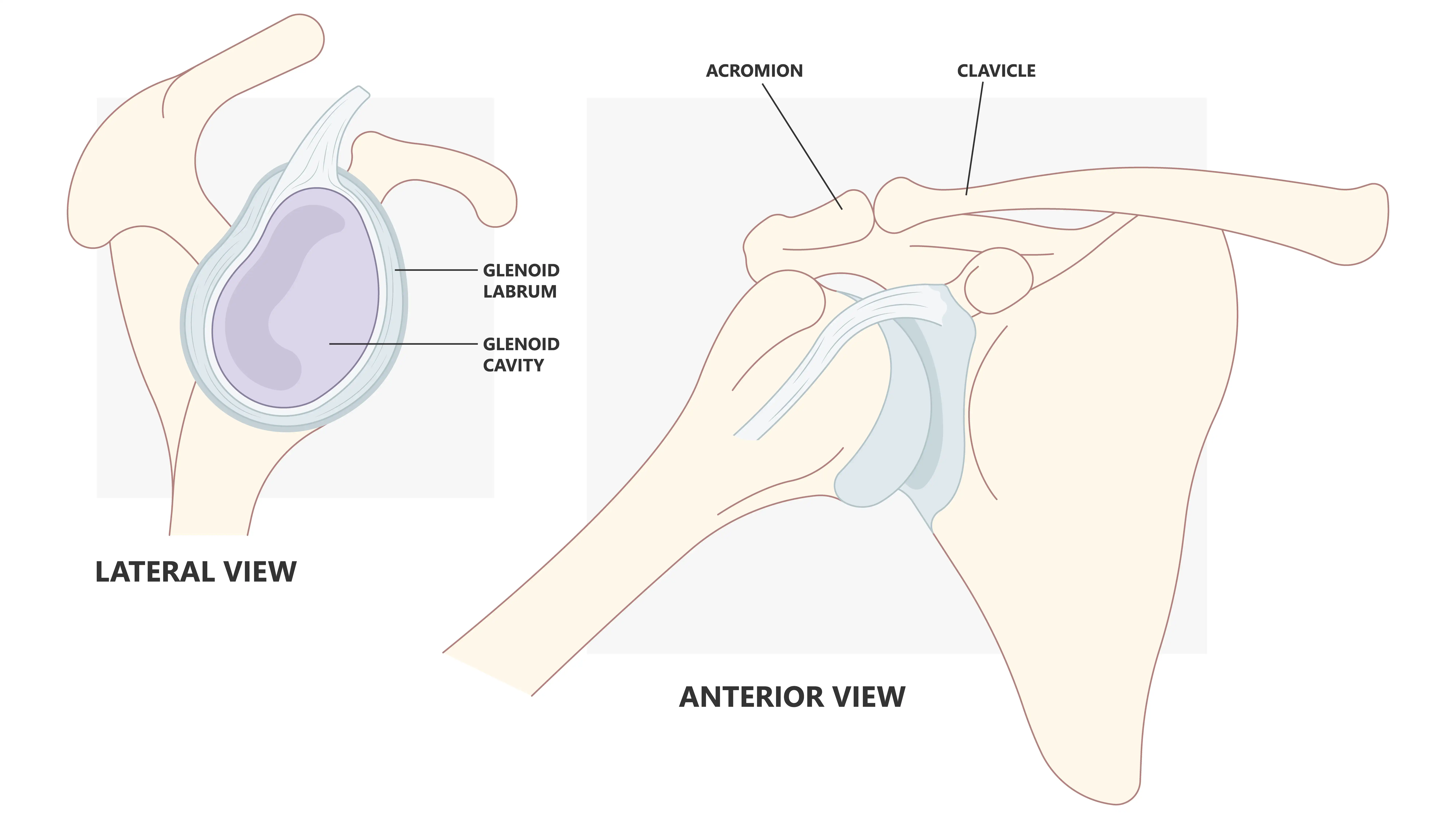
Function of the Glenoid Labrum
This structure provides shoulder stability by deepening the socket depth by approximately 50% and securely holding the humeral head, preventing dislocation. The improved fit and stability of the humeral head support the range of motion of the shoulder joint, especially during complex movements.
The glenoid labrum also acts as a shock absorber, distributing forces evenly across the shoulder joint and reducing stress on surrounding structures. This helps to ensure smooth shoulder operation during high-impact activities like lifting or throwing.
What is a Glenoid Labrum Tear?
A glenoid labrum tear, also known as a labral tear, is an injury to the cartilage surrounding the shoulder socket and can compromise joint stability and function. These tears typically result from acute trauma or repetitive shoulder motion. Understanding the types and causes of these tears is key to proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common Types of Glenoid Labrum Tears
Labral tears are classified based on their location within the shoulder joint. Common types include SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior) tears and Bankart tears.
SLAP tears involve damage to the top part of the labrum where the biceps tendon connects, and these are often linked to repetitive overhead activities. Bankart tears occur at the bottom part of the labrum and are frequently caused by shoulder dislocations. This type of tear can create instability in the shoulder joint, increasing the risk of recurrent dislocations.
Posterior labrum tears, though less common, occur at the back of the shoulder and can also lead to instability.
Causes of Glenoid Labrum Tears
Glenoid labrum tears typically originate from acute trauma or repetitive motion. Acute traumatic events include falls, direct shoulder impacts, or sudden forceful movements like grabbing to prevent a fall. Chronic overuse from repetitive shoulder motions, particularly in athletes who participate in throwing sports or weightlifting, is another common cause.
Age-related degeneration of the cartilage can make the glenoid labrum more susceptible to tearing, and certain sports involving overhead motions (baseball, volleyball, tennis) further increase the risk.
Symptoms of Glenoid Labrum Tears
Recognizing the symptoms of a glenoid labrum tear is important for prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Common symptoms include shoulder pain, instability, grinding, locking, and catching. These symptoms can affect daily activities and overall shoulder function.
Pain and Discomfort
Patients with labral tears often describe an aching or dull pain that may intensify during heavy lifting or overhead motions. Night pain is also common, especially among patients with SLAP tears, where the pain is usually felt at the front of the shoulder near the biceps tendon.
Instability and Limited Motion
A labrum tear can cause instability in the shoulder joint, complicating everyday activities. This instability may come with a reduced range of motion, especially during activities like carrying, pushing, or throwing. Patients with Bankart tears sometimes report feeling a “loosening” of the shoulder and may experience recurrent dislocations.
The combination of pain and instability can create a cycle where limited motion exacerbates weakness, which worsens instability.
Other Indicators
Other symptoms of a glenoid labrum tear include clicking, snapping, or grinding sensations in the shoulder joint. These indicators often accompany pain and instability.
Diagnosing Glenoid Labrum Tears
Accurate diagnosis of glenoid labrum tears requires a comprehensive approach combining physical examination with imaging techniques. While clinical tests provide valuable information, they are often insufficient for a definitive diagnosis, making advanced imaging essential.
Physical Examination
The diagnostic process begins with a thorough examination assessing shoulder stability, range of motion, and pain patterns. These tests help your doctor assess the integrity of the shoulder joint and guide further diagnostic decisions.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging plays a key role in confirming labral tears. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can effectively visualize soft tissue injuries, including tears, but may miss subtle injuries. CT-arthrograms, where a CT scan visualizes the joint after dye has been injected into it, offer another diagnostic option.
Arthroscopy
If a labral tear is suspected despite inconclusive imaging, diagnostic arthroscopy may be recommended. This minimally invasive procedure involves the insertion of a small camera into the shoulder joint to directly visualize the labrum. If a tear is detected, surgeon may be able to repair it through the same small incisions.
Treatment Options for Glenoid Labrum Tears
Treatment for glenoid labrum tears ranges from conservative approaches to surgical interventions, depending on the severity of the tear and the patient’s needs.
Conservative Treatments
The initial approach to treating a glenoid labrum tear typically involves rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy. Corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and manage pain. Physical therapy focuses on gentle range-of-motion and strengthening exercises to aid recovery and restore mobility.
For minor Bankart tears caused by dislocation, a shoulder reduction may be performed to pop the shoulder back in place, followed by a structured physical therapy program to restore shoulder function and prevent future dislocations.
Surgical Interventions
When conservative treatments fail to relieve symptoms, surgical intervention may be necessary. Arthroscopic surgery is often considered for shoulder labrum tears, especially in younger athletes. This minimally invasive procedure uses miniature cameras and small incisions to repair the labrum, leading to quicker recovery and reduced post-operative pain compared to open techniques.
Recovery Process
Recovery from shoulder labrum repair surgery typically takes six months to one year. Athletes are generally advised to wear a sling for three to four weeks post-surgery to protect the shoulder and promote healing. Most patients achieve basic functional recovery within three to four months.
Rehabilitation programs are tailored to each patient, focusing on regaining strength, restoring mobility, and reducing pain. Physical therapy should begin as the swelling diminishes. A physical therapist will recommend exercises specially designed to restore shoulder function and prevent future injuries.
Preventing Glenoid Labrum Tears
Prevention of glenoid labrum tears requires a proactive approach focused on shoulder stability and flexibility. Implementing strategic strengthening exercises and activity modifications can substantially decrease injury risk.
Strengthening Exercises
A shoulder strengthening program forms the foundation of injury prevention. Targeted exercises such as controlled lateral raises with light weights and resistance band external rotations have been shown to improve shoulder stability.
Activity Modifications
To further minimize the risk of a glenoid labrum tear, limit repetitive overhead motions in sports, avoid heavy lifting, and maintain proper throwing techniques. Steering clear of wet or icy surfaces can also prevent slips that may lead to shoulder injuries.
Implementing appropriate activity modifications and safety precautions can protect shoulders from labral tears and other injuries.
Potential Complications from Glenoid Labrum Tears
If left untreated, glenoid labrum tears can lead to complications that negatively affect quality of life. These include chronic pain, persistent shoulder instability, and an increased risk of future injuries. Understanding these potential issues underscores the importance of timely and effective treatment.
Chronic Pain
Persistent shoulder pain is a common consequence of untreated glenoid labrum tears, stemming from ongoing joint damage. This pain typically worsens with time and can lead to significant discomfort and functional limitations, often interfering with daily activities.
Shoulder Instability
A torn labrum can compromise shoulder joint stability, increasing susceptibility to dislocations and subluxations. Dislocations can lead to further labral damage, creating a cycle that becomes difficult to manage without appropriate intervention.
Risk of Future Injuries
Individuals with a history of glenoid labrum tears are at an elevated risk for future shoulder injuries. Larger tears or those left untreated further increase the probability of re-injury. Early intervention and preventive measures can help to mitigate this risk.
Why Choose an Experienced Shoulder Surgeon?
When it comes to diagnosing and treating a glenoid labrum tear, the experience and training of your surgeon can make a difference. Because the shoulder is one of the most complex joints in the body, seeing a specialist who works with shoulder injuries every day increases the chances of getting a precise diagnosis and an effective treatment plan that fits your lifestyle and goals.
An experienced shoulder surgeon can:
· Accurately diagnose difficult or subtle labral injuries
· Offer advanced, precision-based surgical options when needed
· Work closely with physical therapists and sports medicine specialists to create a personalized recovery plan
Choosing a shoulder surgeon with this specialized training can help ensure you receive comprehensive, up-to-date care, whether your treatment is non-surgical or involves a procedure.
Summary
Glenoid labrum tears are a prominent cause of shoulder pain and instability, impacting daily life and athletic performance. Understanding the anatomy and function of the glenoid labrum, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking timely diagnosis and treatment are important steps in managing this condition. Both conservative and surgical treatment options offer pathways to recovery, with prevention strategies playing a key role in reducing the risk of future injuries. Consulting with fellowship-trained surgeons ensures access to the most advanced and effective treatments available, paving the way to recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a glenoid labrum tear?
A glenoid labrum tear is an injury to the cartilage surrounding the shoulder socket, often causing instability and pain. It usually results from trauma or repetitive shoulder motions.
What are the common symptoms of a glenoid labrum tear?
Common symptoms of a glenoid labrum tear include shoulder pain, instability, and sensations of grinding, locking, or catching. Recognizing these signs early is key to prompt diagnosis and treatment.
How are glenoid labrum tears diagnosed?
Glenoid labrum tears are diagnosed through a combination of physical examinations and imaging techniques, particularly MRI and CT-arthrograms. This approach ensures a thorough assessment of the injury for effective treatment planning.
What treatment options are available for glenoid labrum tears?
Treatment options include conservative methods like rest and physical therapy, as well as surgical interventions such as arthroscopic surgery. It’s important to choose the approach that best aligns with the severity of the injury and your lifestyle.
How can glenoid labrum tears be prevented?
To prevent glenoid labrum tears, focus on strengthening shoulder exercises and modify activities to reduce repetitive overhead motions and heavy lifting. Prioritizing these preventive measures can help protect your shoulder health.